Key Points:
- Analysis of MR CLEAN trial focuses on timing of intra-arterial therapy for acute ischemic stroke
- Shorter time to reperfusion associated with better functional outcomes
Patients with acute ischemic stroke achieve better functional outcomes when reperfusion is reached via intra-arterial treatment more quickly, according to new data from the MR CLEAN trial published online December 21, 2015, ahead of print in JAMA Neurology.
MR CLEAN was a randomized open-label trial looking at the effects of intra-arterial treatment added to a background of best medical care in 500 patients (median age 67 years; 58% men) with acute ischemic stroke.
For the current analysis, Diederik W J Dippel, MD, PhD, of Erasmus MC University (Rotterdam, the Netherlands), and colleagues explored whether functional outcomes were influenced by 2 factors: the time from symptom onset to groin puncture as well as the time from treatment initiation to reperfusion (until either reopening of the vessel occlusion or the end of the procedure, if reperfusion was not achieved).
Median values for time to groin puncture and to reperfusion were 260 and 340 minutes, respectively.
Patients were more likely to be functioning independently (modified Rankin Scale [mRS] score 0-2) if reperfused earlier (P for interaction = .04; table 1).
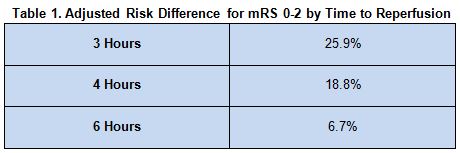
There was no relationship seen between the timing of groin puncture and functional independence (P = .26).
Not an Argument for Withholding Later Treatment
“Our findings reveal a strong inverse relationship between [reperfusion and the effects of endovascular treatment] in patients with acute ischemic stroke caused by a proximal vessel occlusion of the anterior circulation,” write the authors, adding, “Although the treatment effect is highest among patients treated early, our results do not provide arguments for withholding treatment from patients within the 6-hour time window.”
According to the investigators, the findings demonstrate “the critical importance of reducing delays” in providing intra-arterial therapy. “The absolute treatment effect and its decrease over time are larger than those reported for intravenous treatment. For every hour of reperfusion delay, the [absolute risk difference] for chances of a good outcome is reduced by 6%,” they report. “Most important, our findings imply that patients with acute ischemic stroke should undergo an immediate diagnostic workup and [intra-arterial treatment] in case of intracranial arterial vessel occlusion.”
Source:
Fransen PSS, Berkhemer OA, MD, Lingsma HF et al. Time to reperfusion and treatment effect for acute ischemic stroke: A randomized clinical trial. JAMA Neurology 2015;Epub ahead of print.
Disclosures:
- This study was supported in part by the Dutch Heart Foundation and unrestricted grants from AngioCare BV, Covidien/EV3, MEDAC GmbH/LAMEPRO, Penumbra, Inc, and Stryker.
- Dr. Dippel reports that his institution received fees for his role as a consultant for Stryker (speakers bureau/lecture fees).


